ABSTRACT
In cement-based materials porosity plays an important role in determining their mechanical and transport properties. This paper describes an improved low–cost embeddable miniature NMR sensor capable of non-destructively measuring evaporable water loss and porosity refinement in low and high water-to-cement ratio cement-based materials.
The sensor consists of two NdFeB magnets having their North and South poles facing each other, separated by 7 mm to allow space for a Faraday cage containing a Teflon tube and an ellipsoidal RF coil. To account for magnetic field changes due to temperature variations, and/or the presence of steel rebars, or frequency variation due to sample impedance, an external tuning circuit was employed. The sensor performance was evaluated by analyzing the transverse magnetization decay obtained with a CPMG measurement from different materials, such as a polymer phantom, fresh white and grey cement pastes with different w/c ratios and concrete with low (0.30) and high (0.6) w/c ratios.
The results indicated that the sensor is capable of detecting changes in water content in fresh cement pastes and porosity refinement caused by cement hydration in hardened materials, even if they are prepared with a low w/c ratio (w/c = 0.30). The short lifetime component of the transverse relaxation rate is directly proportional to the compressive strength of concrete determined by destructive testing. The r2 (0.97) from the linear relationship observed is similar to that obtained using T2 data from a commercial Oxford Instruments 12.9 MHz spectrometer.
EXPERIMENTAL SECTION
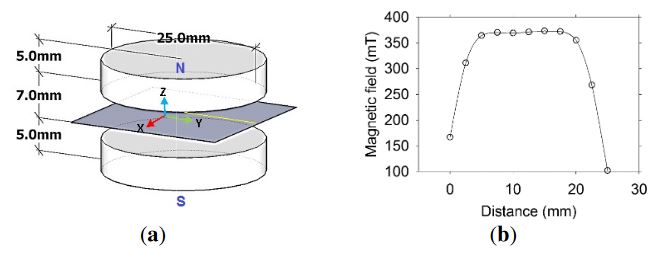
Figure 2. (a) Magnet arrangement for the sensor
Therefore, the sensor has to prevent aggregate particles from entering into its sensitive region. Several magnet arrangements were explored and the Z magnetic field component along the Y-axis (Figure 2) measured to select those providing the highest and the most homogeneous magnetic fields.
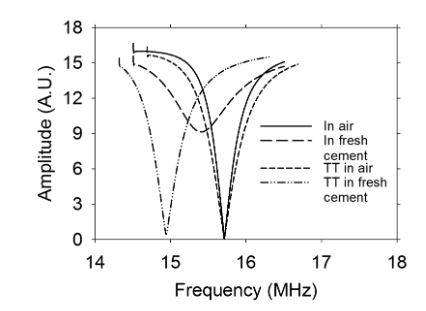
Figure 4. Frequency response of the sensor outside and inside the fresh cement paste w/c ratio = 0.60. TT means sensor with Teflon tube
Figure 4 shows the response in frequency when the sensor without the Teflon tube is immersed in fresh cement paste. There is a change in both frequency and impedance. However, if the Teflon tube is used (could also be a glass tube) there is only a change in frequency. The effect of coupling in impedance and the change in frequency of the coil when it is embedded in the cement paste depends on the characteristics of the material, such as polarity and the dielectric constant.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
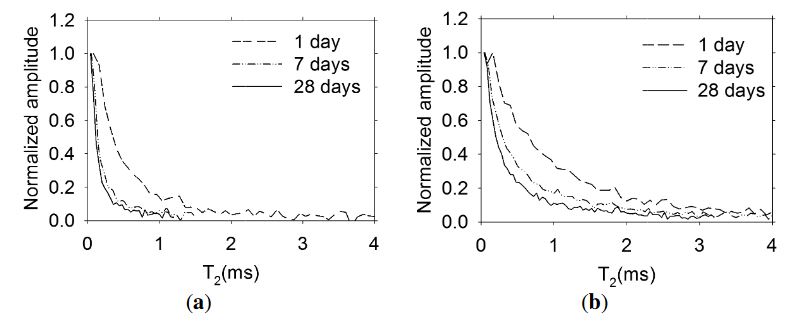
Figure 9. Normalized transverse magnetization decay measured with the embedded sensors in concrete
The normalized transverse magnetization decay at 1, 7 and 28 days of age obtained with the sensors embedded in concrete are shown in Figure 9. A more rapid decay in the specimen prepared with concrete with a w/c ratio = 0.30 is observed. This is expected, since the pores are finer with respect to is observed the higher w/c ratio concrete.
CONCLUSIONS
An improved miniature embeddable NMR sensor for use in cement-based materials was designed, built and characterized. Changes in frequency due to temperature variations and the presence of steel rebars can be accommodated using an external tuning circuit. The sensor was successfully used to detect water in fresh cement pastes and to monitor porosity refinement in hardened cement pastes and concretes containing ordinary materials routinely used in the construction industry. A linear relationship exists between the relaxation rate and the compressive strength of concrete mixtures at low and high w/c ratios. The results demonstrate that practical applications are possible and they will be pursued.
Source: University of New Brunswick
Authors: Floriberto Diaz-Diaz | Prisciliano F. de J. Cano-Barrita | Bruce J. Balcom | Sergio E. Solis-Najera | Alfredo O. Rodriguez