ABSTRACT
The Waterless light fountain is born from the need for art projects for Franklin street in Santa Clara University than is going to be remodeled into an arts and history paseo, one of the ideas discussed was to determine if there may be a way to develop a waterless light fountain that could be displayed either on a temporary or permanent basis. In this paper, we will explain the design process and build of the fountain, using Neopixels (RGB LEDs) to generate the light used as the main art element.
An Arduino is used as the control unit, controlling the Neopixels and receiving input data from the user interface, composed by arcade buttons and a LCD screen with a mounted touchscreen, where users can interact with the fountain by choosing between four different modes of operation, including light shows where LEDs light up in pre-programed sequences, some games as Simon-says or choosing the color of each LED with the help of the touchscreen and light shows combined with music through the performance of a spectrum analyzer controlled by a raspberry pi where the LEDs dance with the music. In the end, the fountain is going to be placed in the engineering building as the design is not minted to endurance the outdoors conditions.
CUSTOMER NEEDS
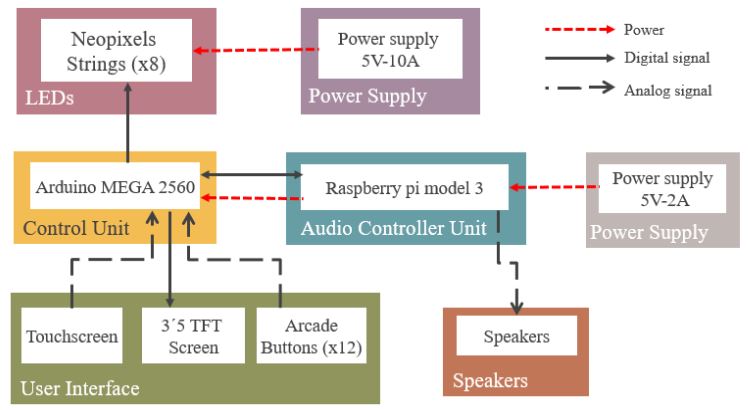
Figure 2.1 Block Diagram
Figure 2.1 shows the high-level design of the waterless light fountain, In the following section we will explain the distinct parts that compound the fountain one by one explaining their functionalities and discussing the design choices of why each component have been selected versus other alternatives, and mentioning those.
DESIGN
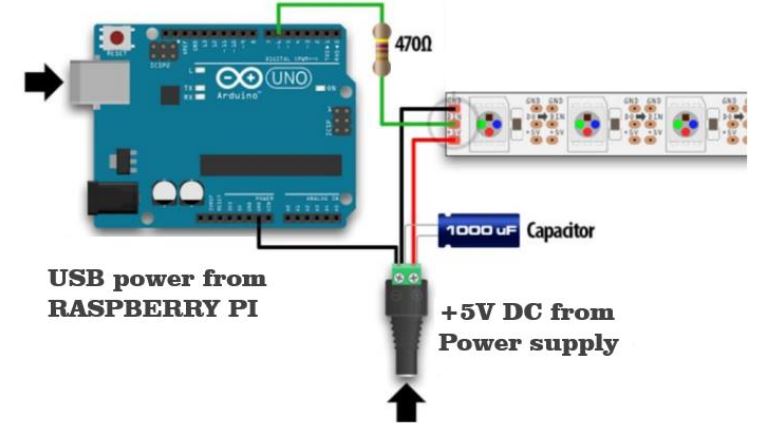
Figure 3.2: Schematics of how to connect each string of Neopixels
When using a DC power supply, the use of a large capacitor across the + and – terminals is recommended Figure 3.2, this prevents the initial on rush of current from damaging the pixels. In our case we are using a capacitor of 1000μF, 12V.
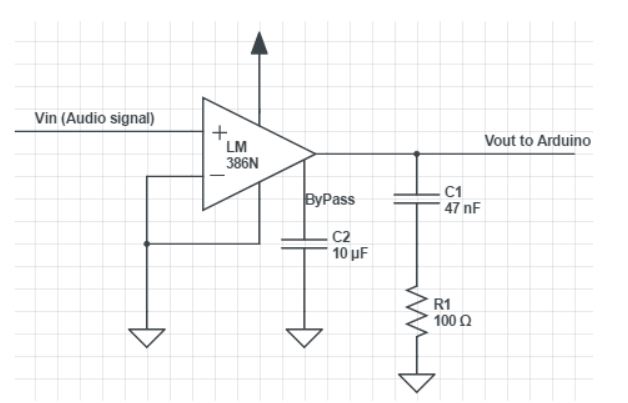
Figure 3.4 : amplifier schematics
Figure 3.4 shows the Amplifier schematics that takes the signal coming from the microphone, and amplifies it having an offset of 2.5 V. F or the microphone as it was only for demo purpose we tried using some that we already had as they were not very good quality the signal had a lot of noise, although for the VU, noise isn’t as important as in other applications, the add of a Bypass between pin 7 and ground with a 10μF (C2) is indicated to prevent supply noise getting back into the earlier amplifier stages.
PHYSICAL DESIGN
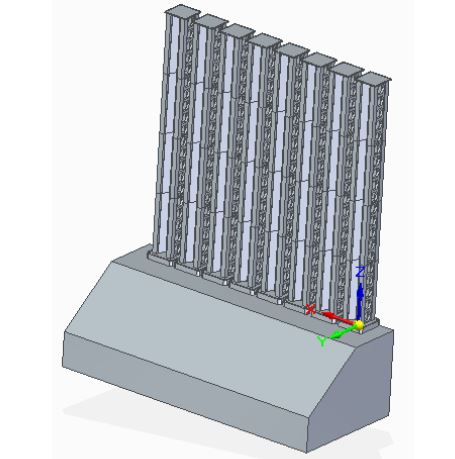
Figure 4.1 Physical Design in Solid Edge
The first idea was to make the waterless light fountain able to endurance outdoors, using acrylic tubes sealed with silicone for placing the NeoPixels strings and make a water-resistant box made of plastic or metal, but due to the dimensions of the fountain and the safety issues as the box is connected to the main, we decided to make it for being inside, to be place in one of the engineering buildings of Santa Clara University.
SYSTEM TESTING AND RESULTS
Due to the nature of the projects constant tests are being perform over and over, as it is a very visual project most of test were easy to validate visually. For the implementation of the system, I worked block by block into the different subsections of the design to integrate them later together.
COSTS
The project cost could be reduced by taking different design approaches, one of the main expenses are the Neopixels which cost could be reduce by selecting cheaper strings of LEDs although the quality may be not as good as with the Neopixels there are definitely cheaper alternatives solutions, also if we get rid of either the raspberry pi or the arduino we will also save some money, either controlling the pixels with the Pi or trying to make a poorer spectrum analyzer that could reproduce wav files from an SD card, wav files could be read by adding a SD card reader module to the arduino, the other alternative could be do it with hardware and although making one PCB is probably even more expensive, if the idea was to make a lot of fountains it will be cheaper and easier to implement in the design, not having to set up the Pi and downloading all the libraries and up loading the songs and the code to it.
PROFESSIONAL ISSUES AND CONSTRAINTS

Figure 6.1 : Waterless Light Fountain Instructions
Also the LED structure fabrication process should be change as the LED towers take lot of time to get 3D printed, so make each tower in one piece and find the appropriate fabrication process. Or create and simpler structure to display the pixels. The fountain is easy to use, very visual and with the instructions Figure 6.1 anyone can know how to use it in less than a minute, so overall, I am really satisfy with usability of the project, is also easy to set up, you only need to plug it to the wall.
CONCLUSION
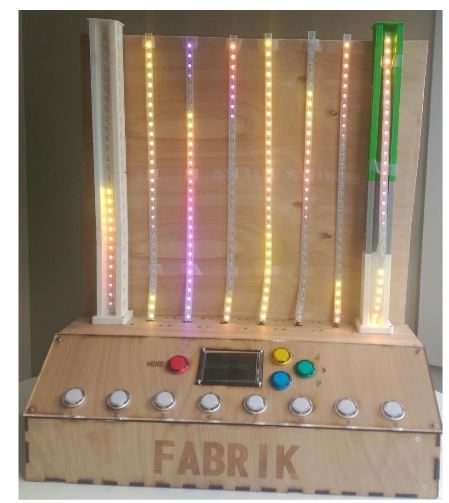

Figure 8.1: Waterless Light Fountain Final Design
We have successfully design and built a waterless light fountain, the fountain satisfies the most important requirements an exception of being able to endurance outdoors conditions such as rain. The different modes are diverse and complete, the user interface is easy to use, the project is compact and is all in a wooden box and although I was unable to 3D print all the LEDs towers it still look pleasant and with a unique style Figure 8.1.
Source: Santa Clara University
Author: Lucas Villalba Eirea