ABSTRACT
Wireless local area network (WLAN) is a technology that combines computer network with wireless communication technology. The 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands in the Industrial Scientific Medical (ISM) band can be used in the WLAN environment. Because of the development of wireless communication technology and the use of the frequency bands without the need for authorization, the application of WLAN is becoming more and more extensive. As the key part of the WLAN system, the antenna must also be adapted to the development of WLAN communication technology.
This paper designs two new dual-frequency microstrip antennas with the use of electromagnetic simulation software—High Frequency Structure Simulator (HFSS). The two antennas adopt ordinary FR4 material as a dielectric substrate, with the advantages of low cost and small size. The first antenna adopts microstrip line feeding, and the antenna radiation patch is composed of a folded T-shaped radiating dipole which reduces the antenna size, and two symmetrical rectangular patches located on both sides of the T-shaped radiating patch.
The second antenna is a microstrip patch antenna fed by coaxial line, and the size of the antenna is diminished by opening a stepped groove on the two edges of the patch and a folded slot inside the patch. Simulation experiments prove that the two designed antennas have a higher gain and a favourable transmission characteristic in the working frequency range, which is in accordance with the requirements of WLAN communication.
DESIGN THEORY
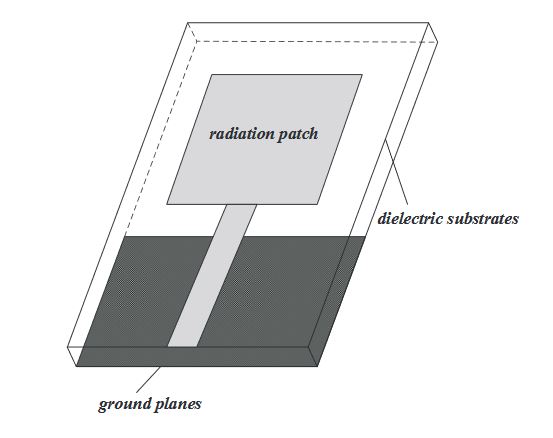
Figure 2. Structure chart of a printed monopole antenna
The typical structure of printed monopole antenna is shown in Figure 2. It has advantages of small size, light weight, easy to integrate and mass production. The feed means of the antenna is microstrip line feeding. The manufacturing process of microstrip line is simple, easy to integrate with other active and passive circuit components, which is conducive to realizing the miniaturization of the circuit system and improving the degree of integration.
DESIGN OF MINIATURIZED DUAL-BAND BROADBAND PRINTED ANTENNAS
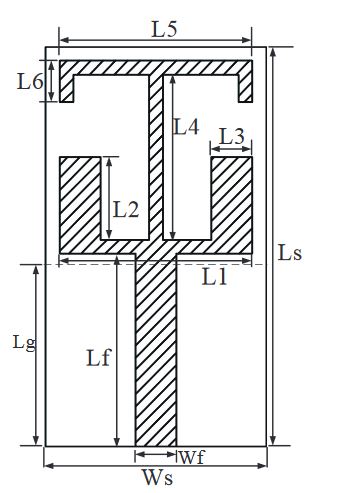
Figure 3. Antenna structure chart
In Figure 3, the structure chart of printed monopole antenna is presented. The antenna is printed on the FR4 antenna substrate with a relative dielectric constant of 4.4. The size of the substrate is Ws × Ls, the thickness is 1.6 mm. The ground plane of the antenna is printed on the back ground of substrate, whose length and width are represented by Lg and Ws, respectively. In addition, the main part of the antenna is printed on the front of the substrate.
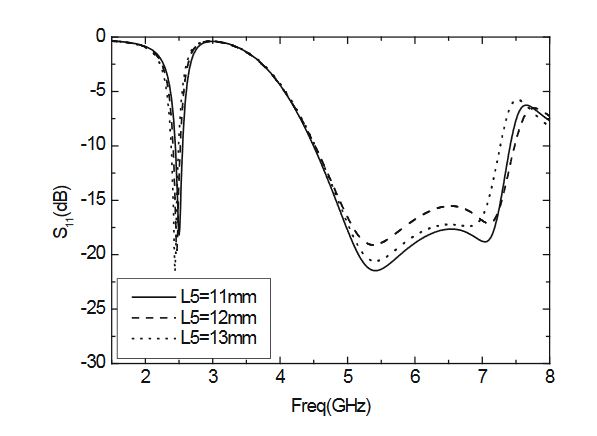
Figure 7. Parameter S11 varies with L5
The length of the horizontal part of the T-sharped element is L5. The value of L5 is changed, and the other parameters are constant, while the changes of S11 with L5 are shown in Figure 7. As shown in the chart, the resonance frequency of the low frequency band decreases with the increasing of L5, and the resonant frequency of the high frequency band does not vary with L5.
DESIGN OF DUAL-BAND MICROSTRIP ANTENNA
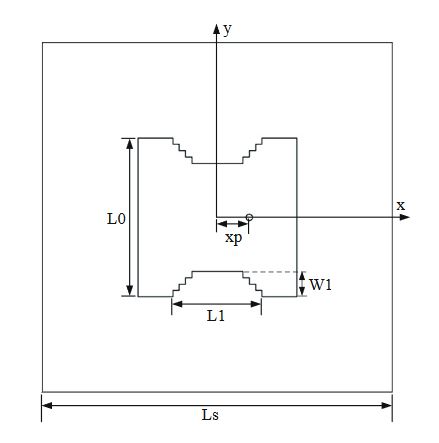
Figure 14. Antenna structure
The antenna structure is shown in Figure 14. The antenna is printed on a square FR4 substrate, the thickness and length of which are 1.6 mm and Ls, respectively. The radiating element of the antenna is a square patch, whose size length is L0. The mode of feeding adopts the coaxial feeding of characteristic impedance 50 Ω, and the distance from the feed point to the center of the patch is xp.
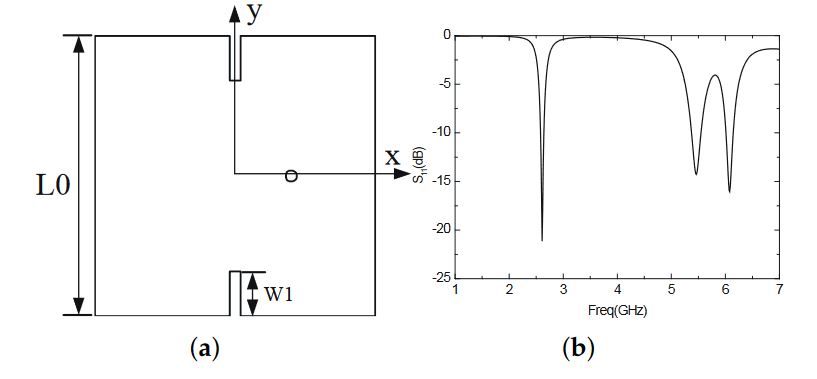
Figure 16. (a) Antenna structure with a rectangular slot; (b) The parameter S11 of the antenna with a rectangular slot
When the antenna is not slotted, the resonant frequency of the antenna is too high. However, the resonant frequency can be moved to the left with the method of slotting, so that the size of the antenna can be reduced. Accordingly, the two edges of the antenna are opened a narrow rectangular groove with a width of 1 mm, a length of W1, as shown in Figure 16a. Figure 16b illustrates the parameter S11 of the antenna under this circumstance. The antenna resonates in the three frequency bands of 2.6 GHz, 5.45 GHz and 6.08 GHz.
CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, two dual-band antennas according to the demand of WLAN for multi frequency communication are designed. One of them is a dual-band printed monopole antenna, which operates in two frequency bands of 2.4 GHz–2.52 GHz and 4.5 GHz–7.5 GHz, and the impedance bandwidth reaches 120 MHz and 3 GHz, respectively, covering 2.4 GHz, 5.2 GHz and 5.8 GHz—three working frequency bands of WLAN. In addition, the gain of the antenna is greater than 4 dB, and the volume of this antenna is only 16 × 29 × 1.6 mm3, implementing the miniaturization of the antenna.
The second antenna is a dual-band microstrip antenna, which works in two frequency bands of 2.4 GHz–2.46 GHz and 5.16 GHz–5.4 GHz, and realizes the miniaturization and dual-band operation by adopting the slotting technology. The two designed antennas have a higher gain and a favourable transmission characteristic in the operating band, which is in accordance with the requirements of WLAN communication under more complicated conditions.
Source: Tianjin University
Authors: Jiachen Yang | Huanling Wang | Zhihan Lv | Huihui Wang
>> 60+ Antenna Communication Projects for Engineering Students
>> HFSS Microstrip Patch Antenna for ECE Final Year Students
>> Final Year Project on Microstrip Antenna for Engineering Students
>> 60+ Final Year Projects on Microstrip Antenna for Final Year Students