ABSTRACT
In the present study, a portable system based on a microcontroller has been developed to classify different kinds of honeys. In order to do this classification, a Simplified Fuzzy ARTMAP network (SFA) implemented in a microcontroller has been used. Due to memory limits when working with microcontrollers, it is necessary to optimize the use of both program and data memory. Thus, a Graphical User Interface (GUI) for MATLAB® has been developed in order to optimize the necessary parameters to programm the SFA in a microcontroller.
The measures have been carried out by potentiometric techniques using a multielectrode made of seven different metals. Next, the neural network has been trained on a PC by means of the GUI in Matlab using the data obtained in the experimental phase. The microcontroller has been programmed with the obtained parameters and then, new samples have been analyzed using the portable system in order to test the model. Results are very promising, as an 87.5% recognition rate has been achieved in the training phase, which suggests that this kind of procedures can be successfully used not only for honey classification, but also for many other kinds of food.
SIMPLIFIED FUZZY ARTMAP
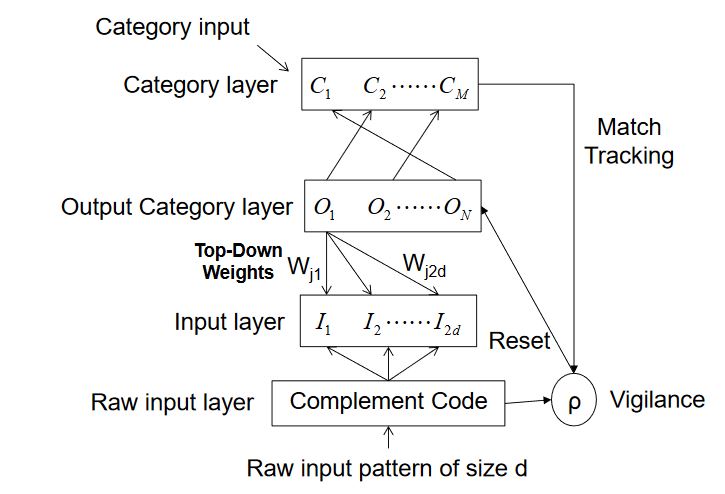
Figure 1. Architecture of the Simplified Fuzzy ARTMAP network
The network is a step forward for Fuzzy ARTMAP in reducing the computational overhead and architectural redundancy. The model uses simple learning equations with a single user selectable parameter and it can learn every single training pattern within a small number of training iterations. SFAM is faster than FAM and it is easier to program. Figure 1 shows the architecture of SFAM. Vectors {a}, with a number of d features, are introduced in the Complement Code.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Different honey samples have been prepared and measured in order to perform the Fuzzy ARTMAP network analysis and its incorporation into a microcontroller. The data were obtained by an electronic tongue system using potentiometric techniques and it consisted of a set of seven metallic electrodes of different materials. The analyses consisted of measuring four different botanic-origin honey samples. Three of these samples were monofloral honey (citric, rosemary and honeydew) and the fourth one was a mix of different origin honeys (polyfloral).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
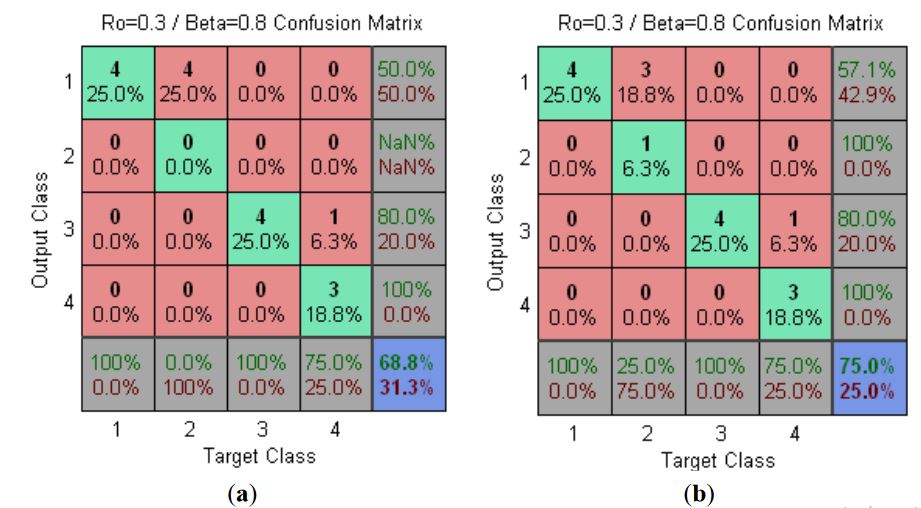
Figure 2. Test data PlotConfusion (seven and four electrodes)
Figure 2 shows the confusion matrix for fuzzy ARTMAP. In this case, a recognition rate of 75% has been obtained. It is interesting to highlight that he microcontroller gave a higher recognition rate when working with a lower number of input variables.
CONCLUSIONS
A Graphical User Interface for MATLAB® has been developed in order to optimize the design parameters of a Simplified Fuzzy ARTMAP algorithm in a microcontroller. The Simplified Fuzzy ARTMAP classification algorithm has been implemented both in Supervised and in its Non-Supervised phase in order to classify honeys. The implementation has been carried out in a portable system based on an 8-bit microcontroller. With the information obtained in the experimental phase, the Simplified Fuzzy ARTMAP network has been trained to obtain the best implementation parameters for microcontroller.
The recognition rate in the Supervised Phase has been 100%. Likewise, a simplification of seven input variables to four has been carried out. With the implemented network in the microcontroller, a test with new samples has been made achieving a recognition rate of 68.8%. This rate has been increased up to 75% by reducing the number of electrodes to four. In addition, this rate could be even higher by increasing the amount of data used in the Supervised Phase. In the end, this study has been carried out with different kinds of honey but the successful obtained results let us predict a similar recognition rate in many other kind of foods.
Source: Jacksonville State University
Authors: Eduardo Garcia-Breijo | Jose Garrigues | Luis Gil Sanchez | Nicolas Laguarda-Miro
>> 200+ Matlab Projects for Control System for Final Year Students